ISO 45001 (OHSAS 18001)
As the Occupational Health and Safety Management System has been adopted as the international standard (ISO 45001), the existing OHSAS 18001(K-OHSMS 18001) will no longer be valid after the migration period (`18.3.12~`21.3.31). Therefore, OHSAS 18001 certified companies must migrate their certification to ISO 45001. K-Certi offers optimal certification services to help you migrate quickly and smoothly.
What is an ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems) certification scheme?
The Occupational Health and Safety Management System involves all employees and stakeholders in order to prevent industrial accidents and create a pleasant working environment. The health and safety management system establishes goals for maintaining and improving the safety and health of employees, and defines the organization, responsibilities and procedures for identifying and managing risk factors inherent in the organization's activities. It makes organization effectively allocate physical and human resources within an organization and manages them systematically.
certification of K-OHSMS 18001/OHSAS 18001 and KOSHA 18001
K-Certi has concluded into a joint certification agreement with the Korea Occupational Safety & Health Agency in the field of Occupational Health and Safety Management System in order to enhance the convenience of the workplace. We jointly issue certificates of both institutions together.
Necessity
- Globalization of Companies: Motives for the Occupational Health and Safety Management System
- Safety as an extension of business processes
- Response to various laws and regulations
- Response to various lawsuits against industrial accidents
- Measure and monitor for continuous improvement
- the duties of entrepreneurs
- Global Public Relations
- Responsibility for stakeholder groups (NGOs)
Expectation effect
- Reduce accident rate by managing and preventing risks in the workplace
- Reduce insurance premiums by establishing a reliable Occupational Health and Safety Management System
- Productivity improvement by improving health and safety risks for workers
- Easy to build integrated system with ISO 9001, ISO 14001
- Easy to enter overseas market by eliminating trade barriers in the safety sector by complying with the standards required
- Reduce export costs by establishing an authorized Occupational Health and Safety Management System that enables mutual recognition agreements
- The awareness of Occupational Health and Safety Management among employers and workers has been developed to the level of advanced countries, and the self-regulated Occupational Health and Safety Management System of companiesis settled as soon as possible.
- Contribute to stabilizing labor-management relations by addressing workers' biased complaints about healthandsafety by obtaining international certification of production products and working conditions
Basic model
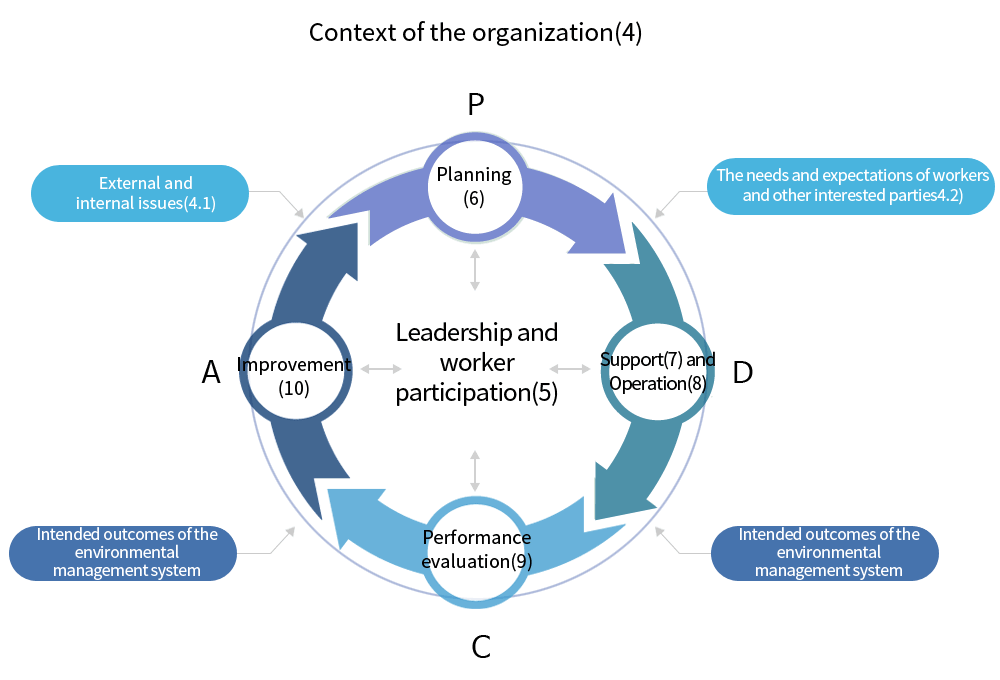
- Plan : Determine and assess OH & S risks, OH & S opportunities, and other risks and opportunities, and establish the required OH & S objectives and processesto produce results consistent with the organization's OH&S policies.
- Do : Execute process according to plan
- Check : Monitor and measure activities and processes related to OH&S policies and objectives and report their results
- Act : Take action to achieve the intended results and to continuously improve OH&S performance
표준 요구사항의 구성
Certification scope
- 03. Food products, beverages and tabacco
- 10. Manufacture of coke and refined petroleum products
- 12. Chemicals, chemical products and fibres
- 14. Rubber and plastic products
- 15. Non-metallic mineral products
- 16. Concrete, cement, lime, and plaster, etc.
- 17. Basic metals and fabricated metal products
- 18. Machinery and equipment
- 19. Electrical and optical equipment
- 22. Other transportequipment
- 23. Manufacturing not elsewhere classified
- 24. Recycling
- 25. Electricity supply
- 26. Gas supply
- 27. Water supply
- 28. Construction
- 29. Wholesale and retail trade; Repair of motor vehicles, motorcycles and personal and household goods
- 30. Hotels and restaurants
- 33. Information technology
- 34. Engineering services
- 35. Other services
- 36. Public administration
- 37. Education