IATF 16949 certification system?
In order to continually improve auto parts-related organizations, prevent non-conformities and reduce scatter and waste, the three big American automakers (DaimlerChrysler, GM, Ford) and European automakers (Peugeot, Renault, Volkswagen, Fiat, BMW) Participated in the IATF (International Automotive Task Force) and formed a quality management system for the automotive industry for the future.
Automotive parent companies and suppliers strongly demanded the need to incorporate various quality management system requirements that have been applied to them (QS-9000 in the United States, VDA 6.1 in Germany, EAQA in France and AVSQ in Italy) into a single internationally accepted quality management system requirement.
Automotive parent companies and suppliers strongly demanded the need to incorporate various quality management system requirements that have been applied to them (QS-9000 in the United States, VDA 6.1 in Germany, EAQA in France and AVSQ in Italy) into a single internationally accepted quality management system requirement.
Necessity
IATF16949 enables integration of existing certifications such as VDA6.1 and AVSQ with just one certification, so suppliers around the world offer high-quality products with minimal time and cost due to many certification acquisition initiatives and The IATF16949 certification represents the certification of the existing Quality Management System, so that the supplier can be more competitive by avoiding the friction with any future customers the specifications.
Expectation effect
- Providing opportunities for product and process quality improvement and securing confidence in international trade
- Redistribution of Supplier's Resources for Quality Improvement
- Access to and maintain consistency of the Quality System of the supply system between the organization and the supplier
- Meeting customer requirements through a single audit of companies dealing in Europe, the United States and Japan in automobile-related industries
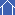
Basic model